Click below to view two clinical update videos presented by: Harold Szerlip MD, MS (ED) FACP, FASN FNKF, CCRP. Director, Division of Nephrology, Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas TX.
Hyponatremia: Clinical update on inpatient treatment.
Hyponatremia: Clinical update on outpatient treatment.
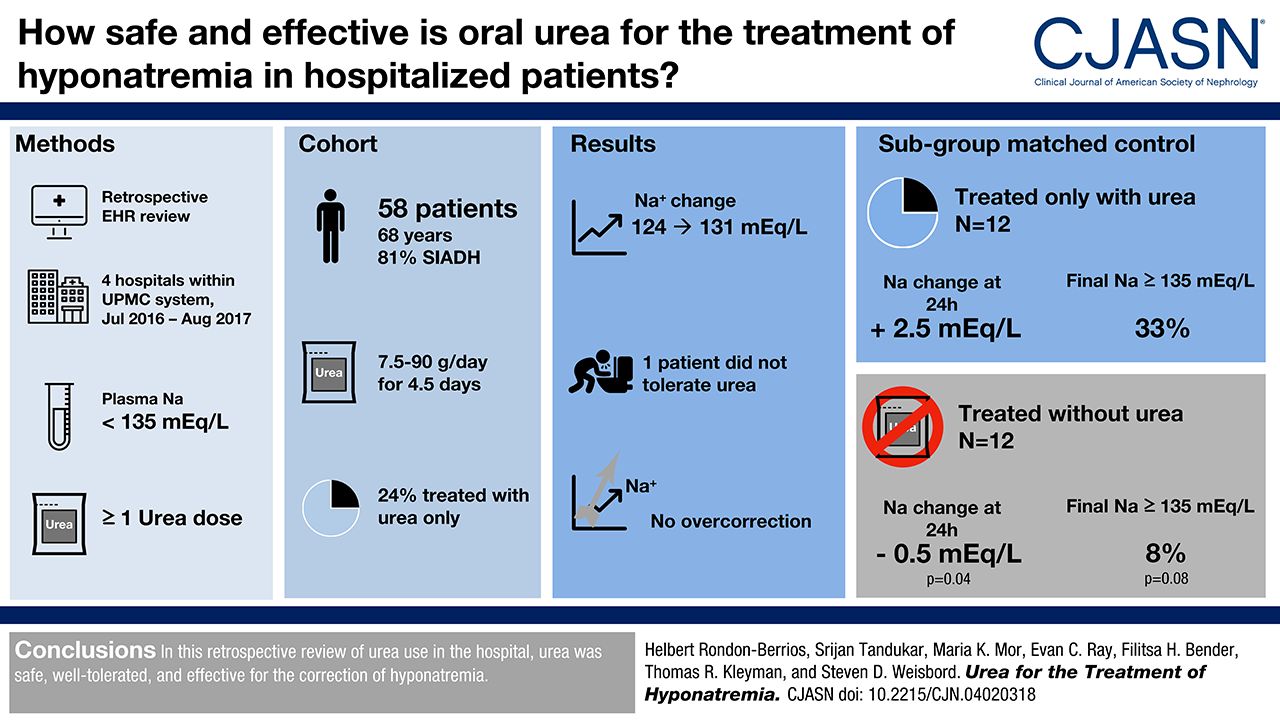
November 2018 CJASN published clinical study on the use of ure-Na to treat hyponatremia in the inpatient setting.
Ure-Na is available in a box with 8 sachets containing 15g USP urea per sachet.

Urea normalizes serum sodium by inducing osmotic excretion of free water without associated electrolyte depletion. Urea also ameliorates hyponatremia in SIADH by a more specific effect, diminishing the natriuresis in association with increased medullary urea content.
Ingredients in descending order: synthetically derived urea powder, natural flavors, maltodextrin, citric acid, calcium silicate, sucralose.
For some, especially people with diabetes the caloric content of ure-Na is important. Each sachet of ure-Na contains less than 15 calories. The calories are derived from the maltodextrin.
A: ure-Na may be covered by health insurance via coverage on the medical side of insurance through Prior Authorization. See the Insurance section for more information. If ure-Na is not covered by insurance, it may be a tax deductible qualified medical expense.
If needed quickly, ure-Na can be ordered at many retail pharmacies and received at the pharmacy the next day. The pharmacist can find ure-Na under item #: 62350-0000-11
If not covered by insurance, ure-Na can be purchased direct or ordered at most retail pharmacies. Patients comfortable ordering online can purchase on this site. Patients not comfortable purchasing online can order by calling 1-844-980-9933. For those paying out of pocket, best price is usually found purchasing direct.
For more information on initiating a prior authorization, please see the insurance section at the top of the home page menu.
For patients with VA benefits, ure-Na is on the VANF (VA National Formulary). Ure-Na is listed as: UREA,PWDR
A: If ure-Na isn't already on formulary at your institutions, ask the inpatient pharmacy to add ure-Na to formulary. Inpatient pharmacy can order ure-Na from their pharmacy wholesaler.
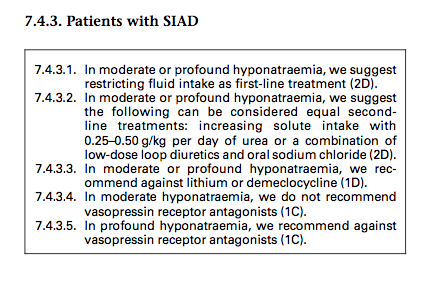
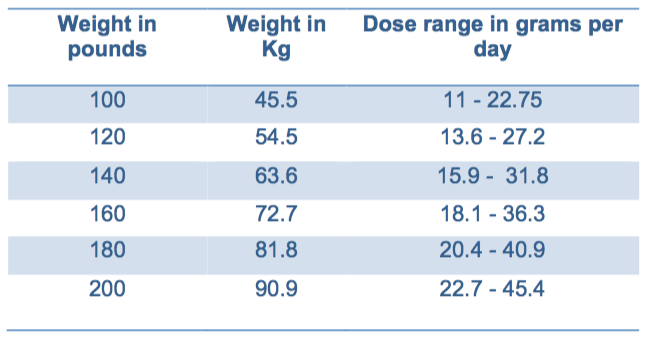
A: The European guidelines* on the use if urea recommend a dose of 0.25-0.50g/Kg (a 140lb person then would take 15.75 - 31.5g) UpToDate discusses a daily dose of 30g of urea.
Typical in-patient dosing ranges between 15-60g/day BIDTypical out-patient dosing ranges between 15-30g/day BID but doses of 60g/day BID are sometimes used. Nephcentric has also received reports from providers about having success dosing ure-Na 15g TIW.A: ure-Na is pharmaceutical grade (USP) synthetically derived urea with a proprietary flavor masking formula, which makes it palatable. It is known that hyponatremia is rarely a sodium deficiency, but rather an excess of water in the blood relative to sodium. Urea normalizes sodium levels in the blood by inducing water loss in the urine. This is accomplished without a risk of loss of important electrolytes like potassium, calcium and magnesium. Treatment with urea is particularly helpful in cases of SIADH (Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion).
A: Guidelines from the European Society of Endocrinology, The European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, and The European Renal Association- EDTA support the use of urea for the management of hyponatremia:(click for link) UpToDate has also reviewed the use of urea in hyponatremia and has recommendations on dosing.(click for link)
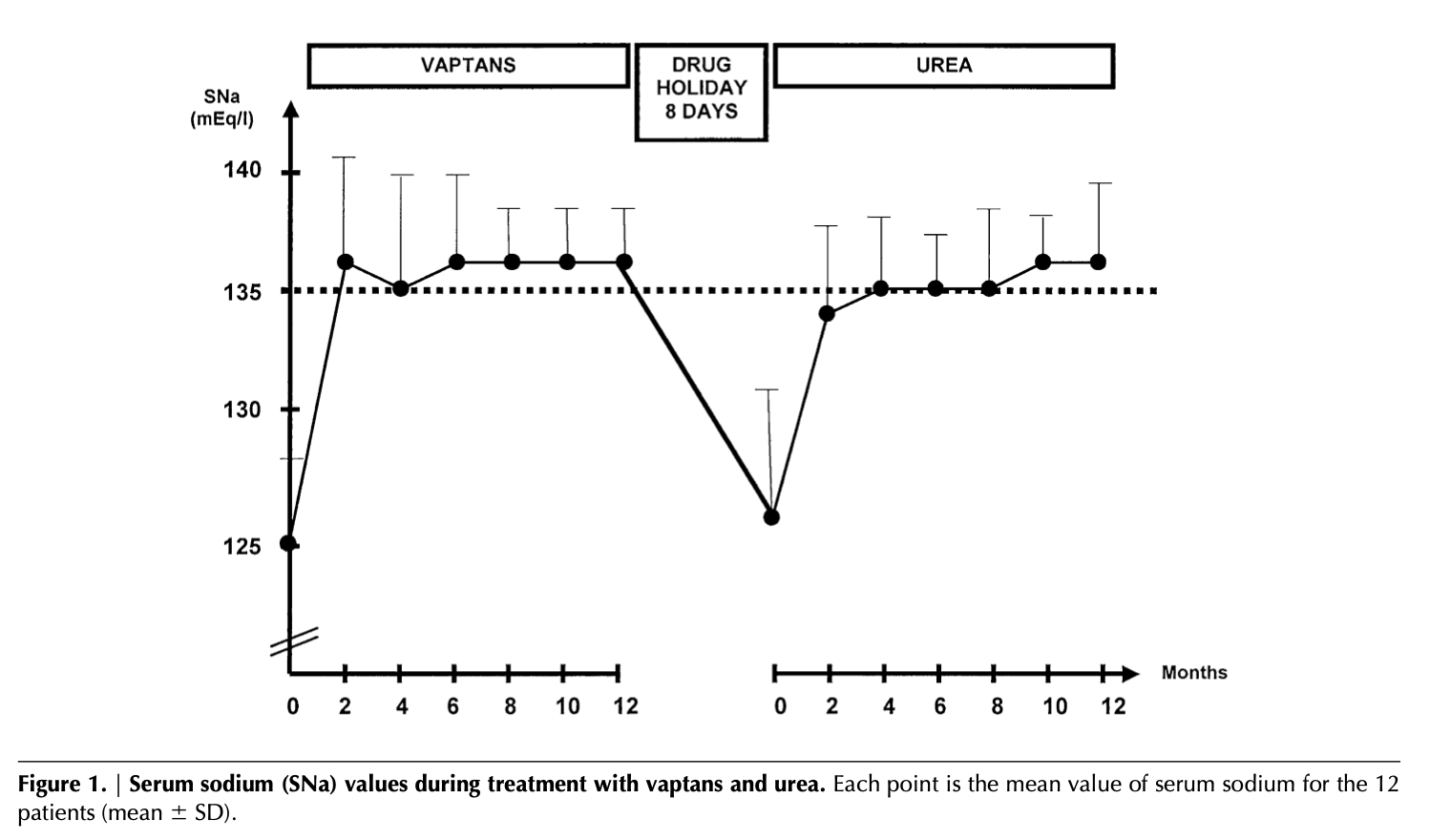
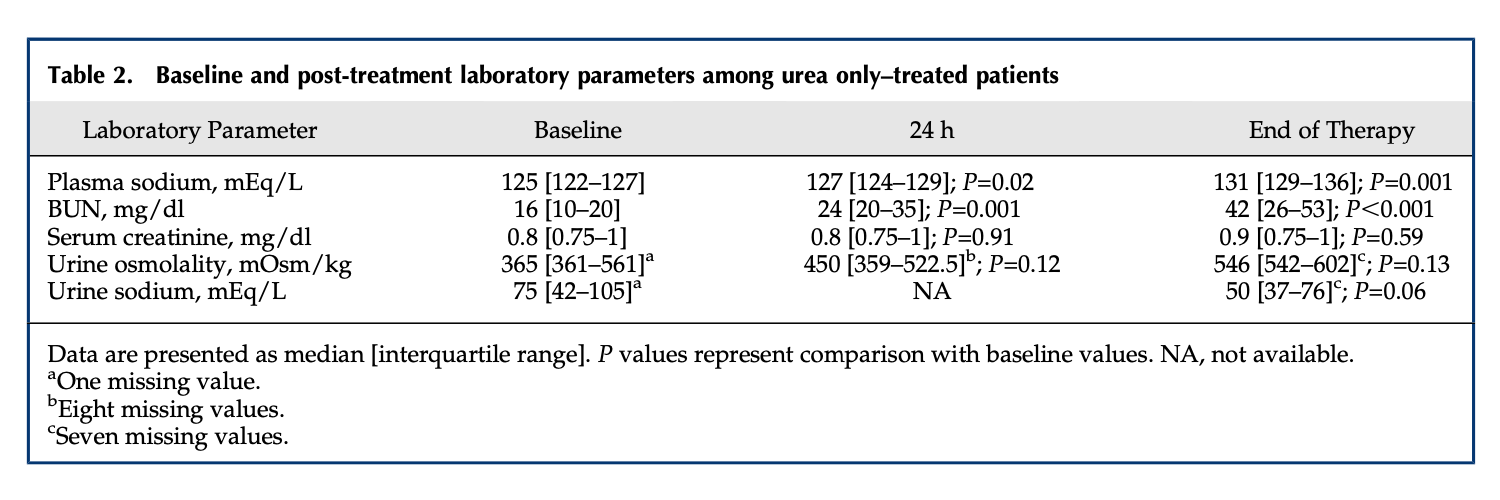
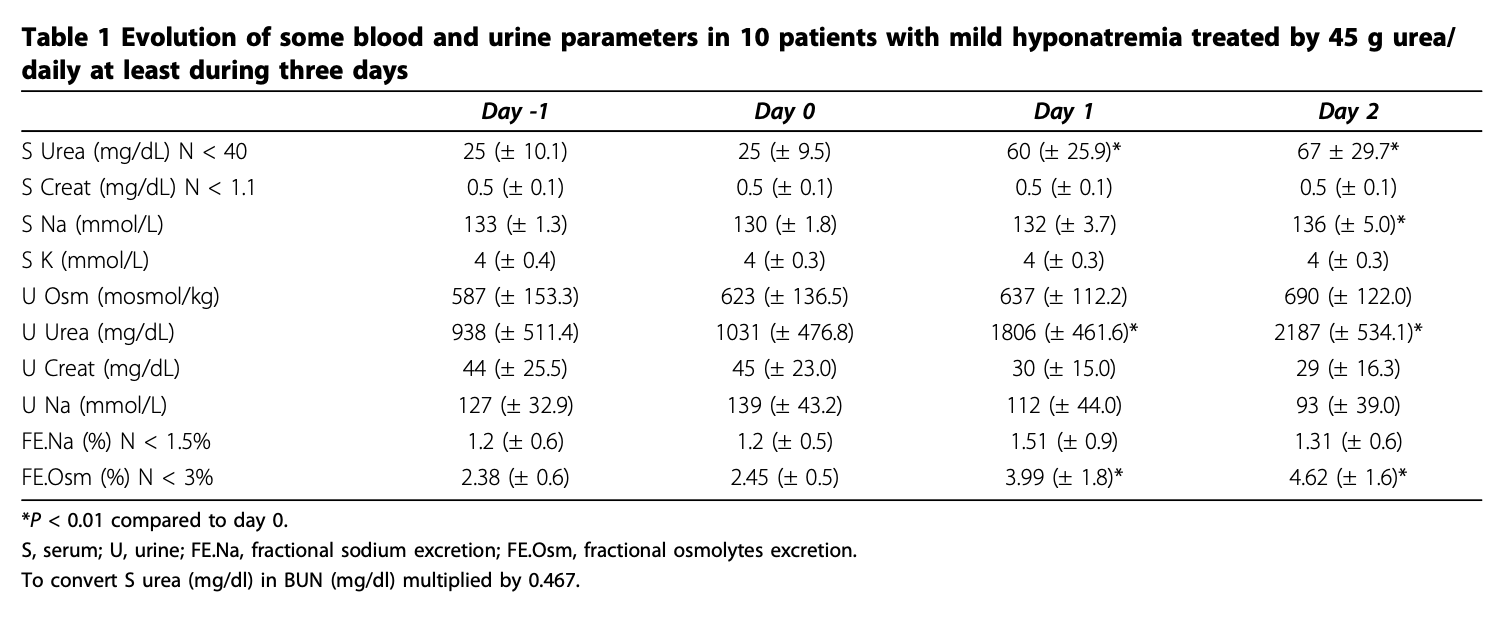
A: In a comparison study of urea versus vaptans, urea had similar efficacy raising serum sodium to 135 mEq/L. (Soupart A: Efficacy and Tolerance of Urea Compared with Vaptans for Long-Term Treatment of Patients with SIADH. CJASN Vol 7 May, 2012.) In another study of the use of urea in an ICU setting, urea raised serum sodium 4 mmol/L the first day of use, and 7 mmol/L in 48 hours. (Decaux et al: Treatment of euvolemic hyponatremia in the intensive care unit by urea., Critical Care 2010 14:R184.) This rate of rise is very important from a safety standpoint, because too rapid a rise of serum sodium levels can be dangerous, and even life threatening. The above study showed that the rise was within the recommended levels of raising serum sodium levels less than 9mmol/L in the first 24 hours.
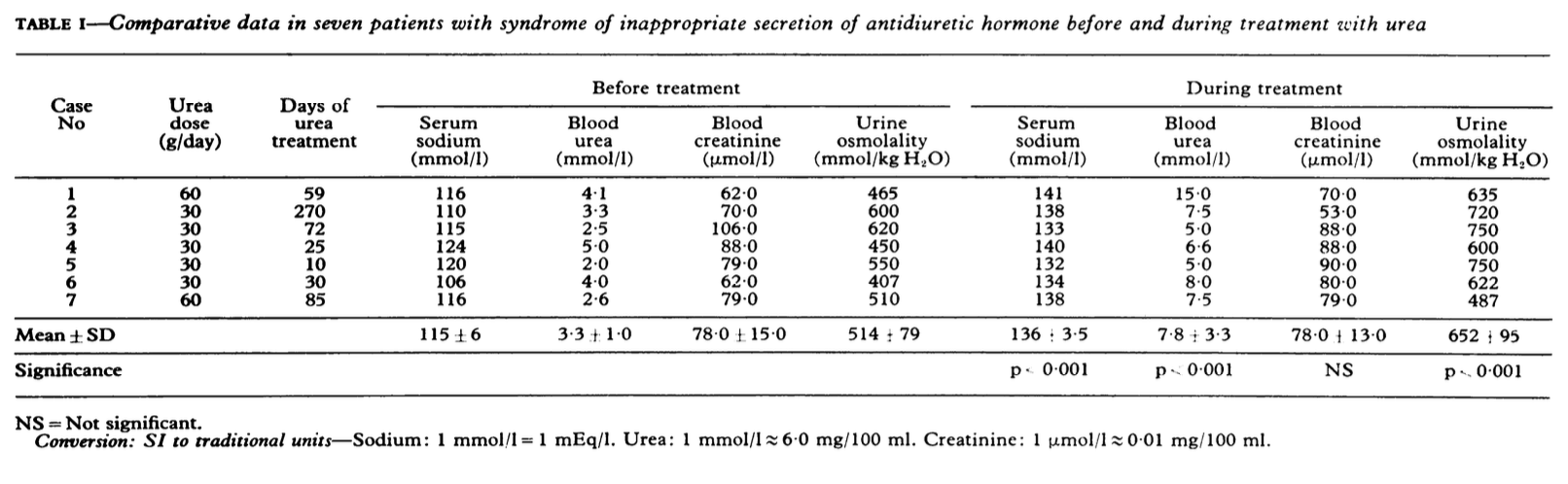
A: The risks of taking urea are very low. No long term toxicity has been seen. There is a very low risk of hypernatremic dehydration if your patients thirst center is intact. (Decaux G: Urea for long term treatment of syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. BMJ Vol 283 24 Oct 1981.).
A: A 15g dose of ure-Na easily mixes into solution with as little as 3-4 ounces of water or juice. As you know, hyponatremia can be a difficult condition to manage. We recommend that ure-Na be taken under medical supervision and that the amount of water or juice that ure-Na is mixed with is determined by the health care provider.
A: Each 15g dose of urea in a single serving of ure-Na is individually packaged in easy to open pouches. There are 8 pouches or doses per box.
A: As each patients therapeutic needs are different, this determination will need to be made by the health care provider
A: The European Guidelines* recommend the use of urea in moderate to profound hyponatremia.
A: Mild GI upset has been seen in a minority of patients taking ure-Na.
A: Urea is not nephrotoxic or hepatotoxic like other therapeutic options for the management of hyponatremia.
A: There is data on the use of urea in doses of 15g and 30g per day for 1 year that show no toxicity. (Soupart A:Efficacy and Tolerance of Urea Compared with Vaptans for Long Term Treatment of Patients with SIADH. CJASN Vol 7 May, 2012)
A: Unlike supplements a medical food, as defined in section 5(b)(3) of the Orphan Drug Act (21 U.S.C. 360ee(b)(3)), is “a food which is formulated to be consumed or administered enterally under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.� Medical Foods, including ure-Na can be purchased OTC without a prescription. Ure-Na is made in the USA in an FDA inspected facility under cGMP guidelines.
A: The FDA classifies urea as GRAS or Generally Recognized As Safe. This is a designation that a chemical or substance added to food is considered safe by experts, and so is exempted from the usual Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) food additive tolerance requirements.